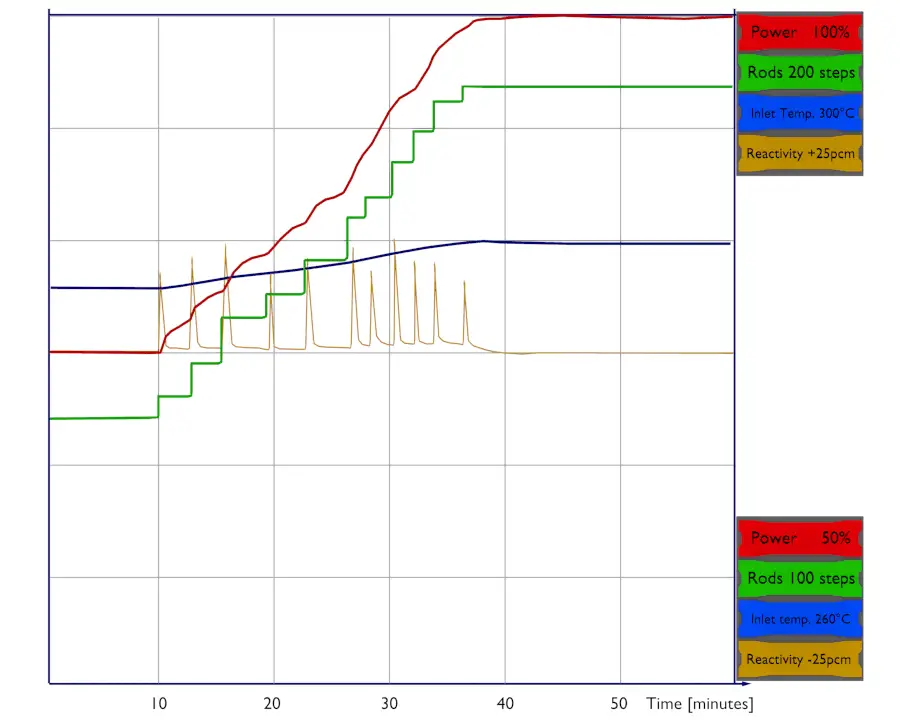
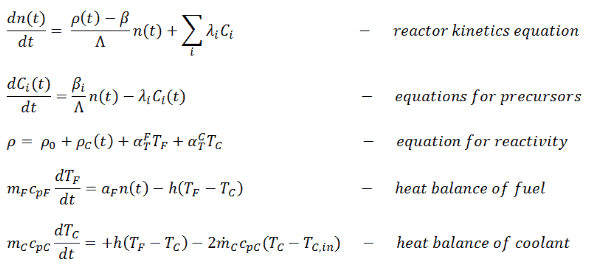A simple point dynamics model is based on point kinetics equations, but we should take into account the influence of the fuel and the moderator temperature on the reactivity. We assume there is no other feedback, and therefore this simple model can be applied only on PWRs. For example, the void coefficient is neglected here. The void coefficient is of prime importance during reactor operation in systems with boiling conditions, such as boiling water reactors (BWR).
Thus, the simplest point dynamics model of PWR should consider the time variations of the fuel and coolant temperature. The point dynamics model consist of the following equations:
- The first equation is the equation for neutrons. The first term on the right-hand side is the production of prompt neutrons in the present generation, minus the total number of neutrons in the preceding generation. The second term is the production of delayed neutrons in the present generation.
- The second equation is the equation for precursors. There is a balance between the production of the precursors of the i-th group and their decay after the constant decay λi. As can be seen, the decay rate of precursors is the radioactivity rate (λiCi). The production rate is proportional to the number of neutrons times βi, which is defined as the fraction of the neutrons that appear as delayed neutrons in the ith group.
- The third equation expresses the dependence of the reactivity on various parameters. But in this case, there is a dependence on the coolant and the fuel temperature only. ρ0 is the initial reactivity, whereas ρC (t) is the time-dependent reactivity inserted by the reactor control system (e.g., by control rods or boron dilution). This is the feedback equation.
- The equations of the heat balance for fuel and coolant are interconnected via h(TF – TC), which represents the heat transfer from the fuel into the coolant. In these equations, mF and mC are the mass of fuel and coolant in the core. Respectively, cpF and cpC are specific heat capacities of fuel and coolant, h is the heat transfer coefficient between fuel and coolant, mC dotted is the coolant mass flow rate [kg/s], and TC and TC,in are the average and inlet coolant temperature, respectively.
To solve the point dynamics equations, it is necessary to specify the initial conditions, like in the case of point kinetics.