Effect of Prompt Neutron Lifetime on Nuclear Safety
The prompt neutron lifetime belongs to key neutron-physical characteristics of the reactor core. Its value depends especially on the type of the moderator and the energy of the neutrons causing fission. Its importance for nuclear reactor safety has been well known for a long time.
The longer prompt neutron lifetimes can substantially improve the kinetic response of the reactor (the longer prompt neutron lifetime gives simply a slower power increase). For example, under RIA conditions (Reactivity-Initiated Accidents), reactors should withstand a jump-like insertion of relatively large (~1 $ or even more) positive reactivity, and the PNL (prompt neutron lifetime) plays here the key role. Therefore the PNL should be verified in a reload safety evaluation process.
In some cases (especially in some fast reactors), reactor cores can be modified to increase the PNL and improve nuclear safety.
See also: Improving Nuclear Safety of Fast Reactors by Slowing Down Fission Chain Reaction
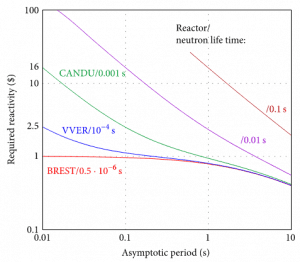 Dependencies of asymptotic time period on the reactivity required for different reactor types with different prompt neutron lifetimes. Source: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijne/2014/373726/
Dependencies of asymptotic time period on the reactivity required for different reactor types with different prompt neutron lifetimes. Source: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijne/2014/373726/Interactive chart – Infinite Multiplying System Without Source and Delayed Neutrons
Press the “clear and run” button and try to stabilize the power at 90%.
Look at the reactivity insertion you need to insert to stabilize the system (of the order to the tenth of pcm).
Do you think that such a system is controlable?