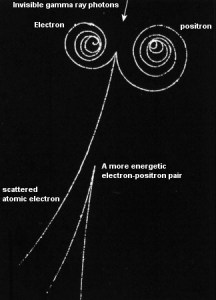
 In general, pair production is a phenomenon of nature where energy is directly converted to matter. The phenomenon of pair production can be view two different ways. One way is a particle and anti-particle, and the other is a particle and a hole. The first way can be represented by the formation of electrons and positrons from a packet of electromagnetic energy (high energy photon – gamma-ray) traveling through matter. It is one of the possible ways in which gamma rays interact with matter. At high energies, this interaction dominates.
In general, pair production is a phenomenon of nature where energy is directly converted to matter. The phenomenon of pair production can be view two different ways. One way is a particle and anti-particle, and the other is a particle and a hole. The first way can be represented by the formation of electrons and positrons from a packet of electromagnetic energy (high energy photon – gamma-ray) traveling through matter. It is one of the possible ways in which gamma rays interact with matter. At high energies, this interaction dominates.
For electron-positron pair production to occur, the electromagnetic energy of the photon must be above threshold energy, which is equivalent to the rest mass of two electrons. The threshold energy (the total rest mass of produced particles) for electron-positron pair production equals 1.02MeV (2 x 0.511MeV) because the rest mass of a single electron is equivalent to 0.511MeV of energy. If the original photon’s energy is greater than 1.02MeV, any energy above 1.02MeV is, according to the conservation law, split between the kinetic energy of motion of the two particles.
The presence of an electric field of a heavy atom such as lead or uranium is essential to satisfy the conservation of momentum and energy. The atomic nucleus must receive some momentum to satisfy both conservations of momentum and energy. Therefore pair production in free space cannot occur. Moreover, the positron is the anti-particle of the electron, so when a positron comes to rest, it interacts with another electron, resulting in the annihilation of both particles and the complete conversion of their rest mass back to pure energy (according to the E=mc2 formula) in the form of two oppositely directed 0.511 MeV gamma rays (photons). The pair production phenomenon is therefore connected with the creation and destruction of matter in one reaction.
Positron-Electron Pair Production – Cross-Section
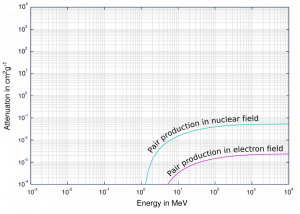 The probability of pair production, characterized by cross-section, is a complicated function based on quantum mechanics. In general, the cross-section increases approximately with the square of atomic number (σp ~ Z2) and increases with photon energy, but this dependence is much more complex.
The probability of pair production, characterized by cross-section, is a complicated function based on quantum mechanics. In general, the cross-section increases approximately with the square of atomic number (σp ~ Z2) and increases with photon energy, but this dependence is much more complex.