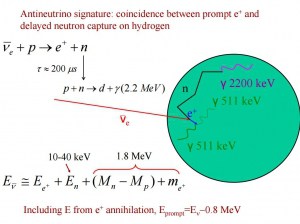
Since neutrinos do not ionize matter, they cannot be detected directly. The antineutrino detection (1995 Nobel Prize for Frederick Reines and Clyde Cowan) is based on the reaction:
![]()
This interaction is symmetrical to the beta decay of the free neutron. Therefore it is sometimes referred to as inverse beta decay. All detection methods require the neutrinos to carry minimum threshold energy of 1.8 MeV. Only antineutrinos with an energy above the threshold of 1.8 MeV can cause interactions with the protons in the water, producing positrons and neutrons.
Reference: Griffiths, David, Introduction to Elementary Particles, Wiley, 1987.
Source: Slides – Dr. Blucher, Enrico Fermi Institute

Photo: Roy Kaltschmidt, LBNL
Source: Daya Bay Reactor Neutrino Experiment